Abstract
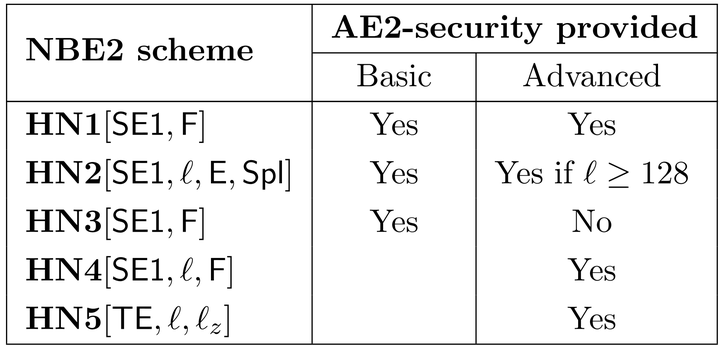
We draw attention to a gap between theory and usage of nonce-based symmetric encryption, under which the way the former treats nonces can result in violation of privacy in the latter. We bridge the gap with a new treatment of nonce-based symmetric encryption that modifies the syntax (decryption no longer takes a nonce), upgrades the security goal (asking that not just messages, but also nonces, be hidden) and gives simple, efficient schemes conforming to the new definitions. We investigate both basic security (holding when nonces are not reused) and advanced security (misuse resistance, providing best-possible guarantees when nonces are reused).
Type
Publication
In International Conference on Applied Cryptography and Network Security (ACNS)